On a summer day in the San Joaquin Valley, 101 in the shade, I merge onto Highway 99 past downtown Fresno and steer through the vibrations of heat. I’m headed to the valley’s deep south, to a little farmworker town in a far corner of Kern County called Lost Hills.
This is where the biggest farmer in America—the one whose mad plantings of almonds and pistachios have triggered California’s nut rush—keeps on growing, no matter drought or flood. He doesn’t live in Lost Hills. He lives in Beverly Hills. How has he managed to outwit nature for so long?
The GPS tells me to take Interstate 5, the fastest route through the belly of the state, but I’m partial to Highway 99, the old road that brought the Okies and Mexicans to the fields and deposited a twang on my Armenian tongue. The highway two lanes here, three lanes there, through miles of agriculture broken every 20 minutes by fast food, gas station and cheap motel.
Tracts of houses, California’s last affordable dream, civilize three or four exits, and then it’s back to the open road splattered with the guts and feathers of chickens that jump ship on the slaughterhouse drive. Pink and white oleanders divide the highway, and every third vehicle that whooshes by is a big rig. More often than not, it is hauling away some piece of the valley’s unbroken bounty.
The harvest begins in January with one type of mandarin and ends in December with another type of mandarin and in between comes everything in your supermarket produce and dairy aisles except for bananas and mangoes, though the farmers here are working on the tropical, too.
I stick to the left lane and stay ahead of the pack. The big rig drivers are cranky two ways, and the farmworkers in their last-leg vans are half asleep. Ninety-nine is the deadliest highway in America. Deadly in the rush of harvest, deadly in the quiet of fog, deadly in the blur of Saturday nights when the field work is done and the beer drinking becomes a second humiliation.
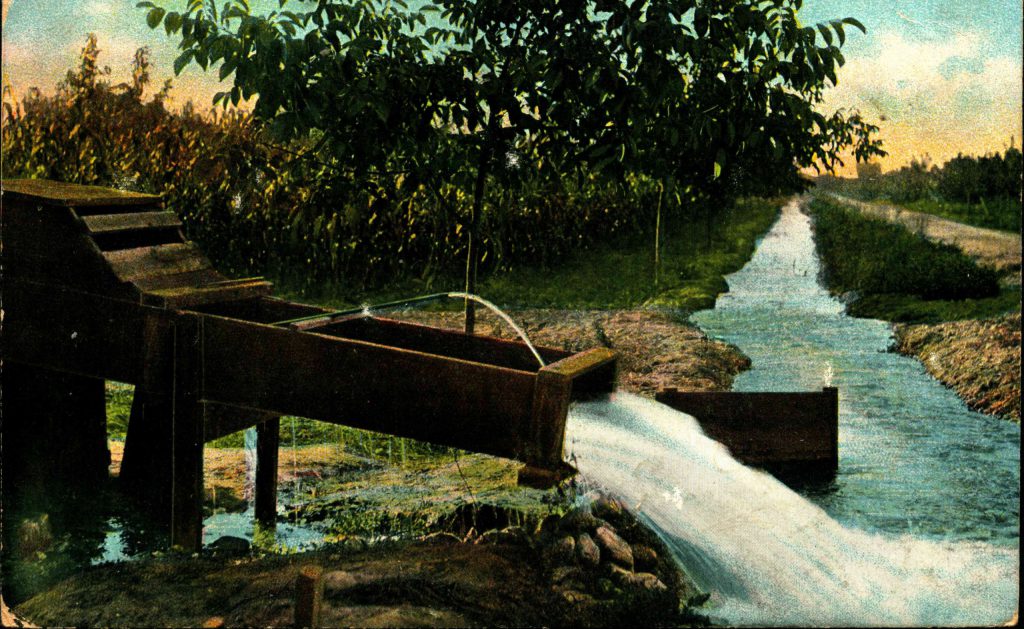
Twenty miles outside Fresno, I cross the Kings, the river that irrigates more farmland than any other river here. The Kings is bone dry as usual. To find its flow, I’d have to go looking in a thousand irrigation ditches in the fields beyond.
There’s a mountain range to my left and a mountain range to my right and in between a plain flatter than Kansas where crop and sky meet.
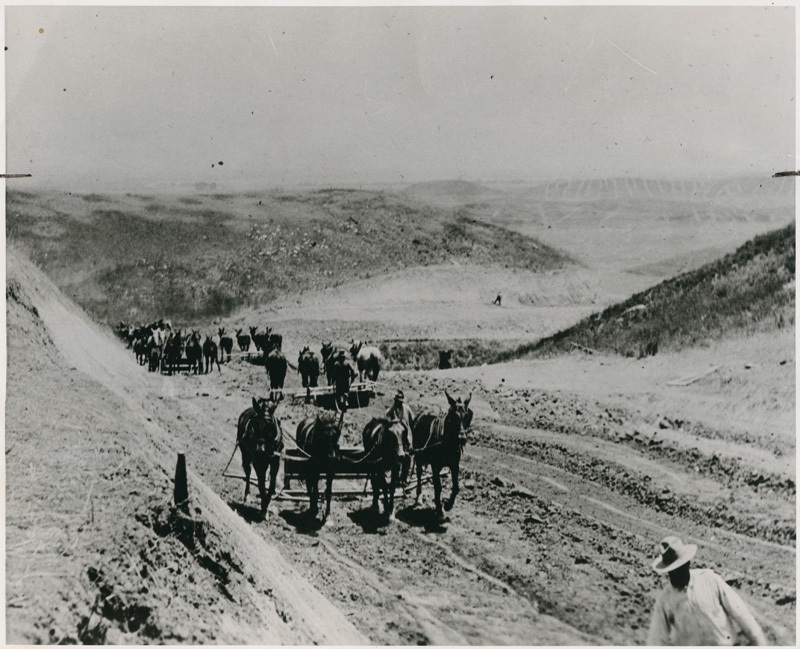
One of the most dramatic alterations of the earth’s surface in human history took place here. The hillocks that existed back in Yokut Indian days were flattened by a hunk of metal called the Fresno Scraper. Every river busting out of the Sierra was bent sideways, if not backward, by a bulwark of ditches, levees, canals and dams. The farmer corralled the snowmelt and erased the valley, its desert and marsh. He leveled its hog wallows, denuded its salt brush and killed the last of its mustang, antelope and tule elk. He emptied the sky of tens of millions of geese and drained the 800 square miles of Tulare Lake dry.
He does this first in the name of wheat, then beef, milk, raisins, cotton and nuts. Once he finishes grabbing the flow of the five rivers that run across the plain, he uses his turbine pumps to seize the water beneath the ground.
As he bleeds the aquifer dry, he calls on the government to bring him an even mightier river from afar. Down the great aqueduct, by freight of politics and gravity, comes the excess waters of the Sacramento River. The farmer moves the rain. The more water he gets, the more crops he plants, and the more crops he plants, the more water he needs to plant more crops, and on and on. One million acres of the valley floor, greater than the size of Rhode Island, are now covered in almond trees.
I pity the outsider trying to make sense of it. My grandfather, a survivor of the Armenian genocide, travels 7,000 miles by ship and train in 1920 to find out if his uncle’s exhortation— “The grapes here are the size of jade eggs”—is true. My father, born in a vineyard outside Fresno, is a raisin grower before he becomes a bar owner.
I grow up in the suburbs where our playgrounds are named after the pioneers of fruit, and canals of irrigation shoot through our neighborhoods to farms we do not know. For half my life, I never stop to wonder: How much is magic? How much is plunder?

Excerpt from The Dreamt Land: Chasing Water and Dust Across California by Mark Arax (http://mark-arax.com/). Published by arrangement with Vintage, a member of Penguin Group (USA), LLC. Copyright © 2020 by Mark Arax.
Mark Arax has been called a “21st Century John Steinbeck” for his books that pry open the soul of California. His unique storytelling—combining history, biography, memoir and reportage—reaches deeply into the land and its people, drawing intimate portraits of farmworkers and farmers and generations of dreamers who come to the “Golden State” seeking a myth only to discover a more brutal truth. A two-time winner of the California Book Award, Arax confronts with lyrical passion a peoples’ defiance of nature that has invented and re-invited California and now imperils its future.